JsWorld
Quick Start
1. Get the software
Get the latest JsWorld version and unpack the ZIP file in a suitable folder on your computer.
2. Create a new HTML document
Start your favourite editor and create a new HTML document in the same directory where you unpacked the JsWorld files.
3. Include the necessary JavaScript files
Put two script
tags into your HTML code, their
src
attributes pointing to:
- The minified file
JsWorld.min.jswhich contains the library classes, all of them packed into a namespace calledjsworldto prevent contamination of the global scope. - The file containing the properties for your chosen locale,
located in the
locales/js/directory. For example, if you need formatting in the en_US locale, then you have to include the filelocales/js/en_US.js.
<script type="text/javascript" src="JsWorld.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="locales/js/en_US.js"></script>
The locale data files have names that correspond to their
locale code, typically in the form
<language_code>_<COUNTRY_CODE>,
and a js extension as they contain JavaScript.
Consult the list
of the available locales for the correct locale codes.
Each locale data file defines a JavaScript object with the number,
currency and date/time format properties of the locale. The object is
named according to the pattern POSIX_LC.<locale_code>,
for example POSIX_LC.en_US for the en_US locale.
4. Formatting numbers
With the above files included the JsWorld library classes and
the locale properties object POSIX_LC.en_US are ready to
use in your JavaScript.
To format a number, you first need to create a new jsworld.Locale
object from the locale data file properties. This is done by passing
the previously loaded POSIX_LC.en_US to its constructor:
// Create locale object from en_US data var locale = new jsworld.Locale(POSIX_LC.en_US);
The jsworld.Locale performs a number of checks on the
raw locale properties and will throw an error if something is wrong,
therefore you should normally use a throw-catch expression to react to
such conditions.
Now create a new numeric formatter, configuring it for the above locale:
var numFormatter = new jsworld.NumericFormatter(locale);
To format a number in the en_US locale, simply invoke the
format method of the NumericFormatter
and pass the value:
alert(numFormatter.format(15000.001));
This should pop an alert box with the correctly formatted number:
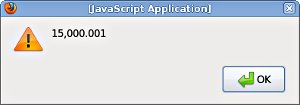
For more information about localised number formatting with JsWorld and the various available options read numeric formatting guide.
5. Formatting currency amounts
To format amounts in the locale's currency, create a new
jsworld.MonetaryFormatter, configuring it with the same
object representing the en_US locale. Then use its format
method as before:
// Format a monetary amount var monFormatter = new jsworld.MonetaryFormatter(locale); alert(monFormatter.format(25000000.99));
You should then see this:
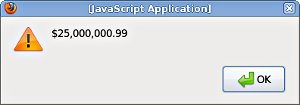
Check the monetary formatting page to learn about the many options for modifying the output, including provisions for ISO-4217 codes and non-local currencies.
6. Formatting dates and times
To format a date or time value you follow a similar procedure -
create a jsworld.DateTimeFormatter object, then use the appropriate
format methods:
// Format current date/time
var dtFormatter = new jsworld.DateTimeFormatter(locale);
var now = new Date();
alert("Current date: " + dtFormatter.formatDate(now) + "\n" +
"Current time: " + dtFormatter.formatTime(now) + "\n" +
"Current date/time: " + dtFormatter.formatDateTime(now) );
The output should look like this:
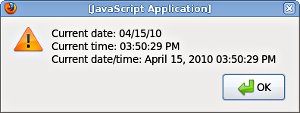
The DateTimeFormatter
also accepts ISO-8601 date/time
strings as input.
7. Parsing
The JsWorld library also includes handy classes for parsing localised number, currency and date/time strings.
Here is how you can parse a USD currency amount formatted according to the en_US locale:
// Parse localy formatted USD currency amount
var monParser = new jsworld.MonetaryParser(locale);
alert(monParser.parse("$1,500,000.01"));
The original amount as a number:
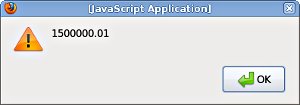
Read the page on parsing for detailed instructions how to use and configure the JsWorld parsers.
8. Things to remember
Summary of the basic steps for working with JsWorld:
- Load
JsWorld.min.jswhich provides all formatting and parsing logic. - Load the required locale properties file from the
locales/jsdirectory. You can load multiple files if you need to work with more than one locale. - Create a new
jsworld.Localeobject from the locale properties. - Create the required formatter or parser, configuring it
with the
jsworld.Localeobject.
9. The complete quick-start example
Here is the complete code for the above formatting examples:
<html>
<head>
<!-- Load JsWorld classes -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="JsWorld.min.js"></script>
<!-- Load definition for selected locale -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="locales/js/en_US.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JsWorld Quick Start Example</h1>
<script>
// Create locale object from en_US data
var locale = new jsworld.Locale(POSIX_LC.en_US);
// Format a number
var numFormatter = new jsworld.NumericFormatter(locale);
alert(numFormatter.format(15000.001));
// Format a monetary amount
var monFormatter = new jsworld.MonetaryFormatter(locale);
alert(monFormatter.format(25000000.99));
// Format current date/time
var dtFormatter = new jsworld.DateTimeFormatter(locale);
var now = new Date();
alert("Current date: " + dtFormatter.formatDate(now) + "\n" +
"Current time: " + dtFormatter.formatTime(now) + "\n" +
"Current date/time: " + dtFormatter.formatDateTime(now) );
// Parse localy formatted USD currency amount
var monParser = new jsworld.MonetaryParser(locale);
alert(monParser.parse("$1,500,000.01"));
</script>
</body>
</html>
10. Further pointers
After going through this quick-start guide you can proceed by looking at:
- The important JsWorld library features and how they may apply to your particular project.
- The complete list of locales for which JsWorld has ready definitions.
- The NumericFormatter manual and API docs.
- The MonetaryFormatter manual and API docs.
- The DateTimeFormatter manual and API docs.
- The parsing manual.